General Medicine Internship Real Patient OSCEs Towards Optimizing Clinical Complexity
This is an a online e log book to discuss our patient de-identified health data shared after taking his / her / guardians signed informed consent. Here we discuss our individual patients problems through series of inputs from available global online community of experts with an aim to solve those patients clinical problem with collective current best evident based input.
This E blog also reflects my patient centered online learning portfolio and your valuable inputs on the comment box is welcome.
I have been given this case to solve in an attempt to understand the topic of " patient clinical data analysis" to develop my competency in reading and comprehending clinical data including history, clinical findings, investigations and come up with diagnosis and treatment plan
The patient/ attender was informed the purpose of the information being acquired. An informed consent was taken from patient/ attender and there is omission of information that was requested to be omitted.
CONSENT WAS GIVEN BY BOTH PATIENT AND ATTENDERS
https://modupallimamatharollno92.blogspot.com/2023/11/50-year-old-female-with-chief.html
Case history :
A 50 year old female came to the medicine opd with c/o loose stools since 4 days and vomitings since 3 days
History of presenting illness :
patient was apparently normal 4 days back then she developed fever which is of high grade , intermittent associated with chills and rigor relieved by medication . Subsided now .
C/o loose stools since 4 days
Watery, non foul smelling, non mucoid , not blood stained 4 to 5 episodes per day
and c/o vomitings 3 days back watery, non projectile , non bilious with food particles as content 4 to 5 episodes subsided now
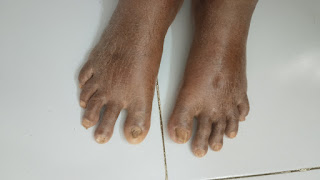
C/o facial puffiness and swelling of upper limb
No H/o cough, cold , decreased urine output , pedal edema,SOB .
No H/o chest pain , palpitations ,orthopnea , PND .
C/0 loss of appetite since 3 days
No H/o constipation.
Past history :
K/C/O DM type 2 since 5 years on tab GLIMI M2 PO/OD HTN since 1 year on tab TELMA 40 Mg PO/OD
N/K/C/O TB, Asthma , Epilepsy , CVA, CAD, Thyroid disorders.
Personal history :-
Diet - Mixed
Appetite - decreased
Bowel and bladder - regular
Sleep - adequate
addictions occasionally alcoholic
Stopped 8 months ago
Stopped smoking chutta 8 months back .
No H/o food and drug allergies
Family history:-
Not significant
General physical examination:
Patient Patient is conscious, coherent, cooperative ,moderately built and nourished
Pallor present , puffiness of face present
No signs of icterus, cyanosis, clubbing, generalised lymphadenopathy
Oedema
Vitals at the time of admission
Temp- afebrile
BP-140/80mmHg
PR- 86 bpm
RR - 18 cpm
SpO2- 99 % at RA
GRBS - 50 mg/dl .......>. After giving 25 D 110 mg/dl
Systemic examination:
CVS- S1;S2 + , no murmurs
RS- BAE+ NVBS heard
P/A- Soft non tender, no organomegaly
CNS :- Patient is arousable , no focal and neurological deficits
Provisional diagnosis :
AKI on ? CKD secondary to acute Gastro enteritis with OHA Induced hypoglycemia with k/c/o DM Type 2 since 5 years,HTN since 1 year
OSCE:
1. General approach to the patient:
1.List all the complaints of the patient with respect to the history and relevant clinical data and mention the treatment plan for each listed problem and mention treatment plan stating it's efficacy in relevance to patient relief and better outcome.
C /o loose stools since 4 days
C/o vomitings since 3 days
K/c/o Diabetes mellitus since 5 years
Hypertension since 1 year
Treatment plan :
IV fluids DNS @ 100 ML/HR
IV FLUIDS 25% D @ 15 ML/HR
INJ CEFTRIAXONE 1g IV /BD
INJ METROGYL 500 MG IV/TID
INJ LASIX 20 MG IV/BD
INJ ZOFER 4 MG /IV/SOS
TAB . CLINIDIPINE 1O MG PO/OD
TAB. SPOROLAC DS PO/TID
2. What are the possible causes of facial puffiness
•Anemia • renal disorders
•angioedema •hypothyroidism• Cushing syndrome
•actinomycosis•cellulitis
3. List out all relevant clinical investigations needed for this patient to make a probable diagnosis
Hemogram:
Chest x ray :
4. What are the different types of AKI , LIST the different criteria required for defining AKI ?
Pre renal AKI
Causes : volume loss( diarrhoea,vomitings ), cardiac issues,sepsis
RENAL AKI : acute tubular necrosis
Drugs,ischemia,snake bite , contrast,tumor lysis syndrome
Acute interstitial necrosis : drugs , infection, myeloma
POST RENAL AKI : obstructive causes
Old criteria : RIFLE CRITERIA
(RISK,INJURY,FAILURE,LOSS,ESRD ). and AKIN CRITERIA
New criteria: KDIGO CRITERIA :
Stage 1: serum creatinine: 1.5 to 1.9 times baseline and urine output less than 0.5 ml/kg /hr for 6 to 12 hrs
Stage 2 : serum creatinine: 2 to 2.9 times baseline and urine output less than 0.5 ml/kg /hr for 12 hrs
Stage 3 : serum cr > 3 times baseline ( > 4 mg/dl )
and urine output less than 0.3 ml/kg /hr for 12 hrs
5 . ORAL HYPOGLYCEMI AGENTS OHA induced HYPOGLYCEMIA is common with which drug ?
Management OHA INDUCED HYPOGLYCEMIA ?
Metformin and thiazolidinediones are highly associated with hypoglycemia
Drug overdose of oha can cause severe HYPOGLYCEMIA which progresses to cerebral hypoglycemia causing severe neurological
Injury or death .
Management:
I.v administraton of glucose
Management of airway , breathing and circulation
6 . Indications for hemodialysis? Different types of dialysis ? Complications occuring during dialysis ? Dialysis dysequilibrium syndrome
Indications for hemodialysis:
Acidosis - metabolic acidosis
Electric abnormality refractory hyperkalemia ,hypercalcaemia
Intoxication barbiturates, alcohol , lithium
Overload - hypervolemia
Uremic encephalopathy, pericarditis , asterixis, seizures .
Types of dialysis :
Acute intermittent hemodialysis
Continuous hemodialysis + ultrafiltration
Peritoneal dialysis
CAPD
CCPD
NIPD
Complications during dialysis:
Intradialytic hypotension:
Due to volume changes
Cardiac factors
Lack of vasoconstriction
Muscle cramps
Dialysis dysequilibrium syndrome
Dialysis dysequilibrium syndrome :
Cerebral edema due to rapid removal of all the urea
Sudden shift in osmolarity
Water moves from blood to cerebral space .
Reactions associated with dialysis:
7 . What is Ckd ? Causes of CKD ? Compications associated with CKD
CKD is loss of cortico medullary differentiation in kidney of size 8 to 10 cm
Or kidney size < 8 cm
Or kidney size > 10 cm with cmd loss In hiv , diabetes,amyloid patients
Causes: diabetic nephropathy
Chronic glomerulonephritis
CTID
COMPLICATIONS: anemia
CAD ( Vascular and cardiac disorders)
Bone mineral disease
Uremic encephalopathy
Uremic neuropathy
HYPOGLYCEMIA
Uremic pruritis
















Comments
Post a Comment